Appendix B: Getting Python 3.x On Your Computer
B.1 Get Anaconda Python
- Although there are several different ways to “get” Python, I am going start by recommending Anaconda Python.
- Anaconda Python is from a company called Continuum Analytics which specializes in open source Python software and support.

- Continuum has easily installable Python packages for Macs, Linux, and Windows.
- Download the Python 3.x version for your operating system.
- Choose 32 or 64 bit versions, depending on your computer.
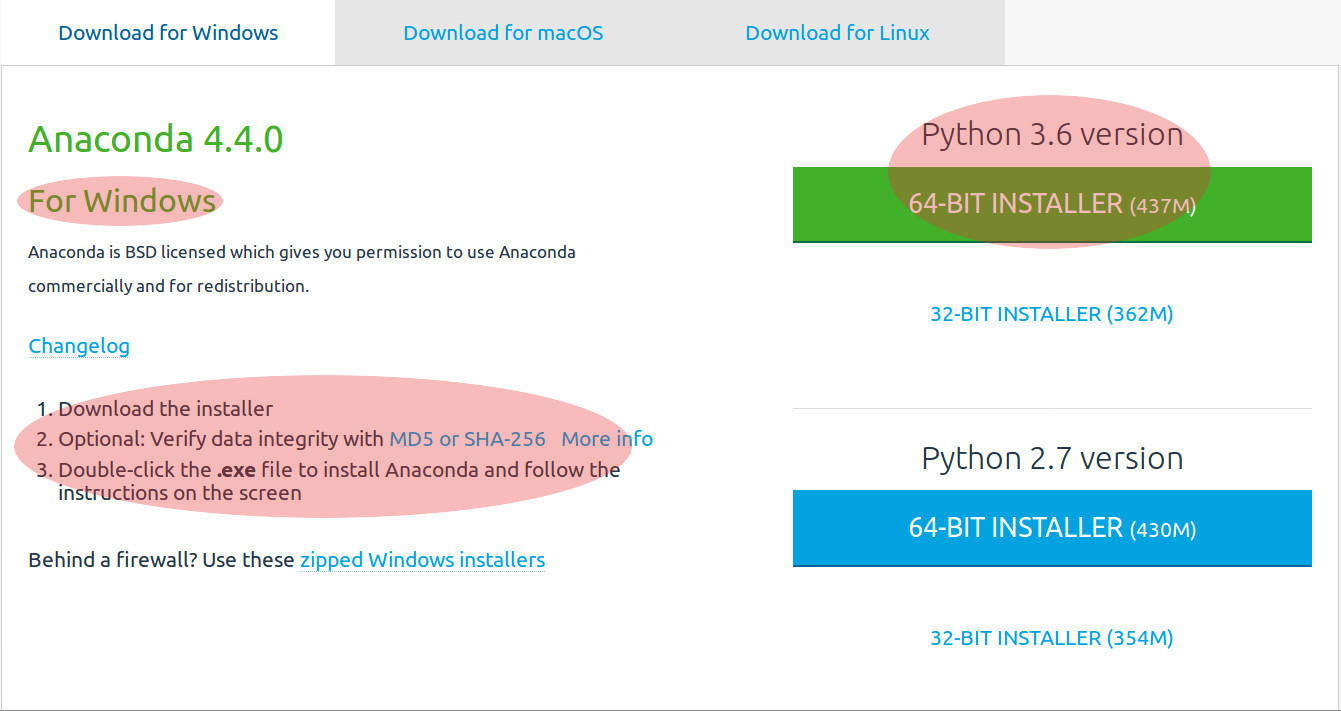
Once you download the Anaconda installer, Install the .exe.
Benefits Of Anaconda
- The major benefit of using Anaconda Python is that it has MANY standard Python libraries which are installed ALL at the same time.
Anaconda Contains:
| Package Title | Example(s) / Uses |
|---|---|
| Biopython | FASTA, GenBank & alignment tools |
| Jupyter / IPython Notebooks | Work & immediately see your results! |
| Spyder | An advanced environment for writing Python |
| Numpy | N-dimensional arrays |
| MatPlotLib | Plot & make graphics |
| Scikit Learn | Machine learning tools |
| Pandas | Work with data structures |
| EVEN Git | Save your work! |
NOTE: The websites for each package or module or library is a good place to start reading & learning about what each does.
So your alternative is to download all these packages and update them yourself or just USE: Anaconda.
What Makes The Computer Language Python Good?
- It is easy use & read because it uses indentation
- Runs on Mac, Windows & Linux …
- “Interpreted” NOT “Compiled”
- Python is interactive, therefore you can see your results right away!
- It has many libraries which can help you with databases, math functions, as mentioned above.
B.2 Excellent Learning Resources:
- Home of Python
- Find Python 3.x Documentation Here
- Learn Python
- Think-Python
- Learn Python the Hard Way # Very good site despite the name.
- Codecademy
- Dive into Python
- Code School
- This is course material suggested # Steven Salzberg
- Python Scientific Lecture Notes # If you don’t read anything else, read these.
- NumPy for Matlab users START here.
- Lectures on Scientific Computing # Great Python Jupyter Notebooks.
- A Byte of Python # A very good book, at the introductory level.
- StackOverflow
B.3 The Very Basics of Programming Strategies
General Steps
- Identify the required inputs, such as data or specifications
- Make an overall design for the program, including listing all the steps by which the program computes the output.
- Decide what will be the output of the program.
- Refine the overall design by specifying more detail.
- Write the program.
- Adapted from Beginning Perl for Bioinformatics by James Tisdall, O’Reilly Media, Inc., 2001
Designing a Program
Write pseudocode for a program that computes the GC percentage composition of a DNA sequence:
- read DNA sequence from user, dna = open(“dna.txt”)
- count the number of C’s in DNA sequence, dna.count(“C”)
- count the number of G’s in DNA sequence,dna.count(“G”)
- determine the length of the DNA sequence, len(dna)
- compute the GC%, g_c_content = \( \frac{(dna.count("C") + dna.count("G"))}{len(dna)} \)
- print GC%