Chapter 2 - Get in touch with Gaia
2.1 How to try Gaia
The quickest way to try Gaia is via Firefox WebIDE (for Firefox 33 above) or Firefox App Manager.
Firefox WebIDE is a developer tool available in Firefox for Desktop. It provides a number of useful tools to help you test, deploy and debug HTML5 web apps on Firefox OS phones and the Firefox OS Simulator, directly from your browser.
In desktop Firefox Browser 33+, open the WebIDE from MENU > Tools > Web Developer > WebIDE. Select a runtime from the menu and you are ready to experience Firefox OS.
The whole viewable and responsive things in the Simulator are done by Gaia.
2.2 How to get Gaia Source
It’s possible to only get gaia source, run it with a nightly browser or simulator, and flash it without modifying Gecko. First, you need to have a windows/mac/linux PC or laptop with git installed.
You should fork the main Gaia repository to your own. It’s better to register a github account so you can contribute your code back to gaia and keep code in a maintainable way.
Click the ‘fork’ button in top right corner to fork to your own repository from https://github.com/mozilla-b2g/gaia. Now you can clone the code from your forked repository:
1 $ git clone https://github.com/gasolin/gaia.git
And remember to run the following command in that folder:
1 $ git remote add upstream https://github.com/mozilla-b2g/gaia.git
to add remote mozilla-b2g/gaia as upstream to your git remote repository.
2.2.1 How to keep gaia up to date
Once you have mozilla-b2g/gaia in your git remote repository, you can run the command
1 $ git remote update
to update all remote repository.
Then run the command
1 $ git merge upstream/master
to make your local file up to date.
2.3 Run Gaia via Firefox nightly
Get and install the Firefox nightly version (codenane: mulet) from http://ftp.mozilla.org/pub/mozilla.org/b2g/nightly/latest-mozilla-central/.
The file is named like firefox-xxx.en-US.mac64.dmg.
Then execute the following commands in the gaia directory:
1 $ DEBUG=1 make
2 $ [app path]/firefox -profile [gaia absolute path]/profile-debug
It will bring up a new firefox nightly window, with a Firefox OS frame in it.
Gaia provides a desktop-helper addon, which has a mockup of the Firefox OS
device environment and provides some useful tools.
The addon allows us to test and debug Gaia code in the browser and reuse all web tools.
2.4 How to install Gaia on a real device
Make sure your device is rooted. Then you have to enable the remote debug console before installing gaia on the device.
2.4.1 Enable the remote debug console
Firefox OS reuses the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) of Android Open
Source project (AOSP) and accordingly inherits some low-level debug tools from AOSP, such as adb (Android Debug Bridge).
To install gaia on a real device, you need have adb tool installed. adb is a command line tool that lets you communicate with the device.
On your device, check settings > Device Information > More information > Developer Menu. Then go back to top level of settings, and you’ll see the developer panel. Click it, then select the Remote Debugging option as ADB and Devtools.
It will enable the remote debug console and enable you to debug your device with the App manager.
2.4.2 Setup adb
WebIDE already wraps the adb helper
addon
for gaia developers. Connect your device via USB, and then tap connect button in WebIDE to connect with your device.
If you like to use adb via command line, you can install adb manually.
Open http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html, click DOWNLOAD FOR OTHER PLATFORMS and download SDK Tools only for your platform.
Unzip it in your path and You can find the adb tool in <sdk>/platform-tools/.
To make it work with gaia build tools, edit PATH environment in windows,
edit ~/.bash_profile in mac OS X, or the correspondent file in Linux distributions.
Let’s take OS X for example, edit ~/.bash_profile:
1 export PATH=${PATH}:<absolute sdk path>/platform-tools
Save and reload the environment. Then you can type ‘adb’ in command line to test if it works.
Once adb is settled, you can install gaia into a real device.
2.4.3 Install Gaia on a real device
First connect your device to your computer with a USB cable.
To check if there is any connected device, you can type:
1 $ adb devices
2 List of devices attached
3 emulator-5554 device
If there’s a device attached, you can proceed with the running following commands. If you see no connected device with the above command, you (Windows or Linux distributions user) may need to check OEM USB Drivers page to correctly set up the USB driver on your computer.
Clean Install
Run the following command to reset your phone with your gaia source code
1 $ make reset-gaia
In 2.2 or above, we can add an extra parameter P=1 to enable multiprocess compiling.
1 $ make reset-gaia P=1
It will be way faster.
Install apps without reboot
To test non-system apps, you can install them without rebooting the device. Just run the command
1 $ make install-gaia
Install a specific app within gaia
If you want to install a specific app only, you can pass it through the APP variable:
1 $ make install-gaia APP=browser
2.5 Debug with a real device
You still need the APP manager or adb tool to remote debug the apps on a Firefox OS Device.
Firefox OS share the same console.log() command as normal web pages do. You can see the same log as in the Firefox Web Console
1 $ adb logcat
To clean up the log entries
1 $ adb logcat -c
To show the Error log entries only:
1 $ adb logcat | grep "Error"
or filter with -s option to achieve the same output result
1 $ adb logcat -s "Error"
The full adb tools usage is available on Android Debug Bridge page. Note that some android specific command may not work on Firefox OS devices.
2.6 Gaia source structure
Here’s the quick overview of the code structure and functionality.
apps/
all main gaia apps, including the apps shown in homescreen, such as calendar, camera, and fundamental apps such as system, homescreen, and keyboard
build/
contains build scripts
dogfood_apps/, external-apps/, showcase_apps/, test_apps/
folders containing other apps that will be included in customization.
Firefox marketplace is located in external-apps. It’s developed separately and is included as a packaged app.
keyboard/
keyboard dictionaries and layouts for different languages.
locales/
localization files for different languages.
shared/
Files that are shared over the Gaia and will be included in build time
tools/
tools for build script and test.
2.7 How a WebApp gets started
All build-in WebApps are packaged webapps, which are essentially zip files containing all application assets: HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, manifest, etc. Each WebApp in gaia is organized with the following structure:
1 apps/[app name]/
2 - js
3 - styles
4 - locales
5 - test
6 - index.html
7 - manifest.webapp
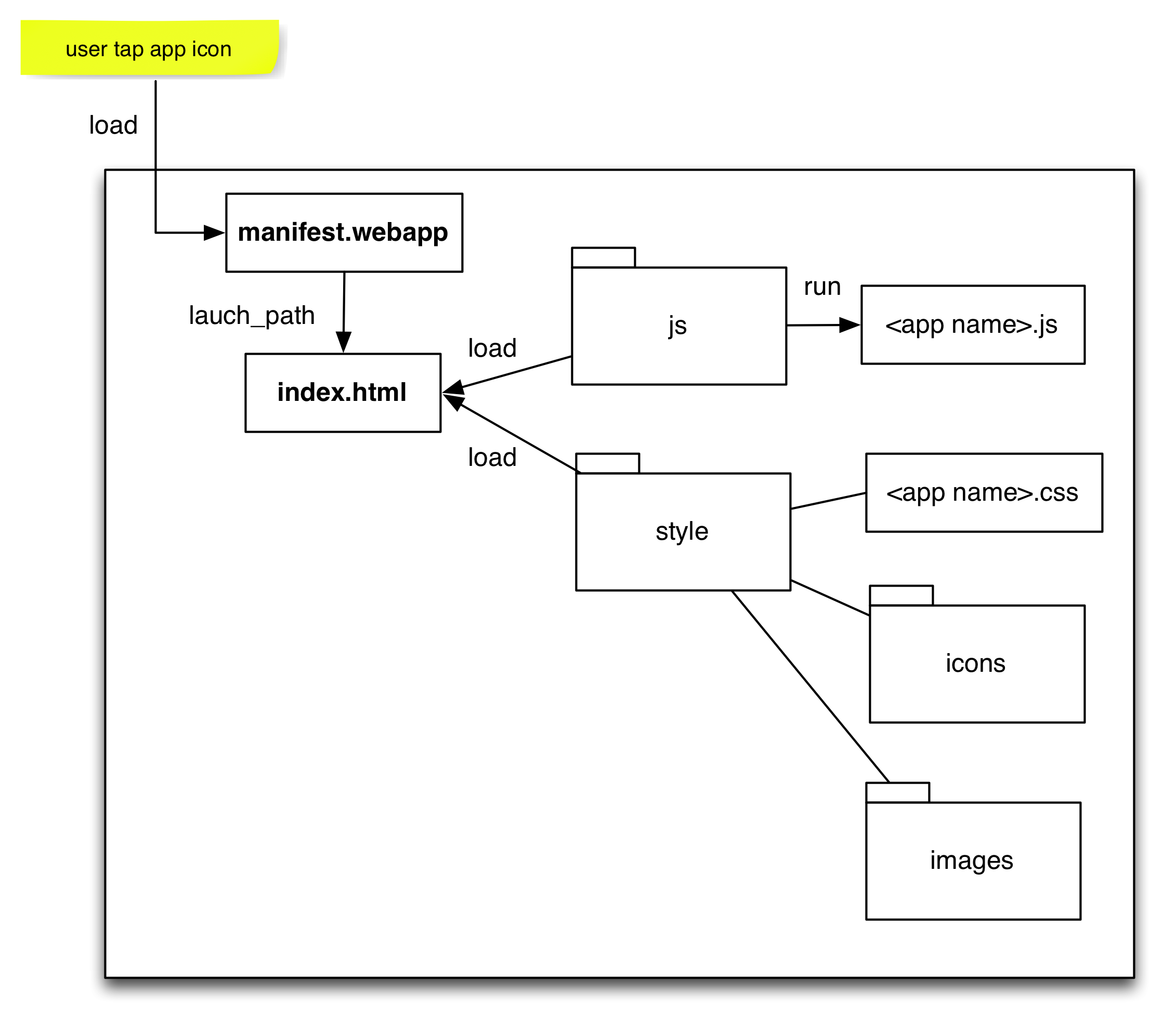
webapp load process
Once the system app tries to launch a built-in webapp, it will try to open the manifest://[app name].gaiamobile.org:8080 URL.
Gecko will try to parse the manifest.webapp within a webapp. manifest.webapp defines the launch path, and by convention it’s index.html for all build-in webapps. The index.html file will load the required styles and javascript.
You can refer to the manifest format from MDN.
2.7.1 js
All javascripts are located in the /js folder.
As an informal convention, the major javascript entrypoint will be named as [app name].js or main.js.
2.7.2 styles
All app related styles are located in the /styles folder.
2.7.3 locales
App-related language/localization strings are located in the /locales folder.
The localization is done with shared/js/l10n.js, which wraps the navigator.mozl10n API and changes the strings to the translated versions in the locales/*.properties files.
A general string will be
1 <span data-l10n-id="hello">hello</span>
The data-l10n-id attribute specifies a key which maps to a value inside of a properties file. This content is changed after the page loads.
You can refer to Localizing Firefox OS Apps for more detail.
The official translations are maintained separately in https://hg.mozilla.org/gaia-l10n.
2.7.4 tests
App-related test cases are located within the /test folder.
Check Chapter 4 for more about running tests.
2.8 How to contribute to Gaia
Gaia is an Open Source project. You can help this project with a variety of skills you’d like to perform such as documentation, testing, coding, marketing and so forth.
If you are not sure if Gaia is the project you’d like to work on, it’s ok. There’re plenty of Mozilla related projects that can help you do good with other people. Consult the What can i do wizard first.
2.8.1 Find a bug to contribute
If you expect to fix something in gaia, check the Bugzilla to see if it has been done before you actually do it.
Mozilla uses the Bugzilla issue tracking system to track issues and bugs. It’s an essential tool to manage large-scale projects.
Bugzilla is the single place to track all Mozilla-related bugs, including Firefox OS/Gaia bugs
Here’s a good reference of using bugzilla and a more tips and hacks of using bugzilla.
You can check the good first bug list, which are picked by experienced Mozilla developers. They are willing to mentor and help you fix some first easy bugs, to get familiar with the developing environment and how to contribute to these open source projects.
2.8.2 File a bug
The best ways to get contributing to an Open Source project is to file a bug.
Filing a bug allowing you to tell people that something is broken or a new thing you would like the project to do. It also introduces yourself to the existing community.
In the guide of writing a good bug, bugs can be categorized into two categories:
- Reporting errors
- Asking for new features or enhancements
There’s a specific https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/Firefox_OS/Developing_Firefox_OS/Filing_bugs_against_Firefox_OS that shows how to file a Firefox OS bug.
Talk more on IRC & bugzilla to update your findings and how to analyze the issue.
Once you are committed to contribute to the Gaia project, there’re addon tools featuring github integration:
- https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/github-tweaks-for-bugzilla/?src=search
- https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/bugzillajs/
2.9 Reference
- Gaia Development Cycle
- Different ways to run Gaia (https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/Firefox_OS/Developing_Gaia/Different_ways_to_run_Gaia)