1. Thinking in tmux
In the world of modern computing, user interaction has 2 realms:
- The text realm
- The graphical realm
tmux lives in the text realm in which fixed-width fonts appear in a rectangular grid in a window, like in a terminal from the 1980s.
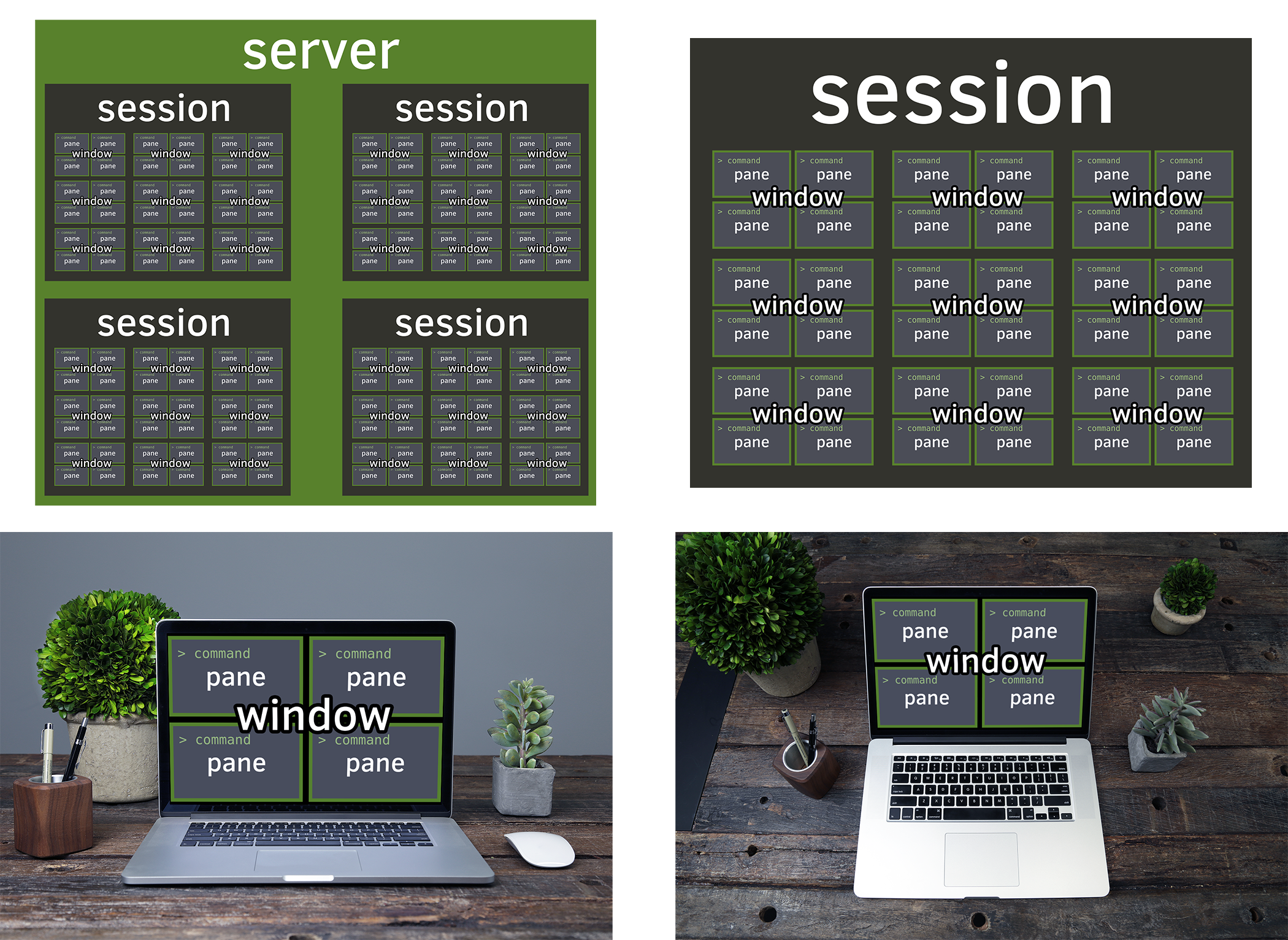
Window manager for the terminal
tmux is to the console what a desktop is to GUI apps. It’s a world inside the text dimension. Inside tmux, you can:
- multitask inside the terminal, run multiple applications
- have multiple command lines (pane) in the same window
- have multiple windows (window) in the workspace (session)
- switch between multiple workspaces, like virtual desktops
| tmux | “Desktop”-Speak | Plain English |
|---|---|---|
| Multiplexer | Multi-tasking | Multiple applications |
| simultaneously. | ||
| Session | Desktop | Applications are visible here |
| Window | Virtual Desktop or | Desktop containing its own screen |
| applications | ||
| Pane | Application | Performs operations |
Just like in a graphical desktop environment, they throw in a clock, too.
Multitasking
tmux allows you to keep multiple terminals running on the same screen. After all, the abbreviation “tmux” comes from - Terminal Multiplexer.
In addition to multiple terminals on one screen, tmux allows you to create and link multiple “windows” within the confines of the tmux session you attached.
Even better, you can copy and paste and scroll. No requirement for graphics either, so you have full power, even if you’re SSH’ing or on a system without a display server such as X.
Here are a few common scenarios:
- Running
$ tail -F /var/log/apache2/error.login a pane to get a live stream of the latest system events. - Running a file watcher, like watchman, gulp-watch, grunt-watch, guard, or entr. On file change, you could do stuff like:
- Keeping a text editor, like vim, emacs, pico, nano, etc., open in a main pane,
while leaving two others open for CLI commands and building via
makeorninja.
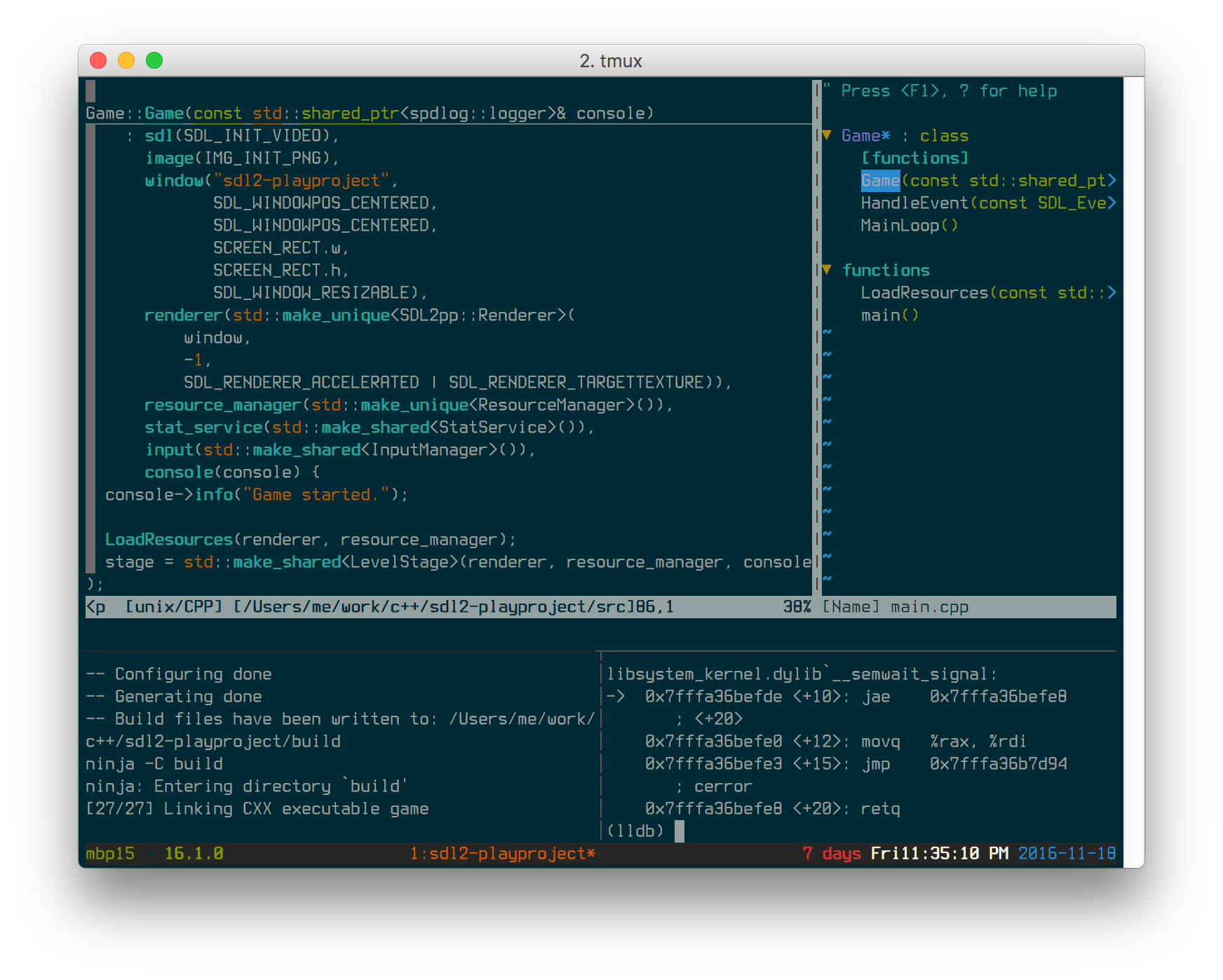
With tmux, you quickly have the makings of an IDE! And on your terms.
Keep your applications running in the background
Sometimes, GUI applications will have an option to be sidelined to the system tray to run in the background. The application is out of sight, but events and notifications can still come in, and the app can be instantly brought to the foreground.
In tmux, a similar concept exists, where we can “detach” a tmux session.
Detaching can be especially useful on:
- Local machines. You start all your normal terminal applications within
a tmux session, you restart X. Instead of losing your processes as you
normally would if you were using an X terminal, like xterm or konsole, you’d
be able to
tmux attachafter and find all the processes inside that were alive and kicking all along. - Remote SSH applications and workspaces you run in tmux. You can detach your tmux workspace at work before you clock out, then the next morning, reattach your session. Ahhh. Refreshing. :)
- Those servers you rarely log into. Perhaps, a cloud instance you log into 9
months later, and as a reflex,
tmux attachto see if there is anything on there. And boom, you’re back in a session you’ve forgotten about, but still jogs your memory to what you were tweaking or fixing. It’s like a hack to restore your memory.
Powerful combos
Chatting on irssi or weechat, one of the “classic combos”, along with a bitlbee server to manage AIM, MSN, Google Talk, Jabber, ICQ, even Twitter. Then, you can detach your IRC and “idle” in your favorite channels, stay online on instant messengers, and get back to your messages when you return.
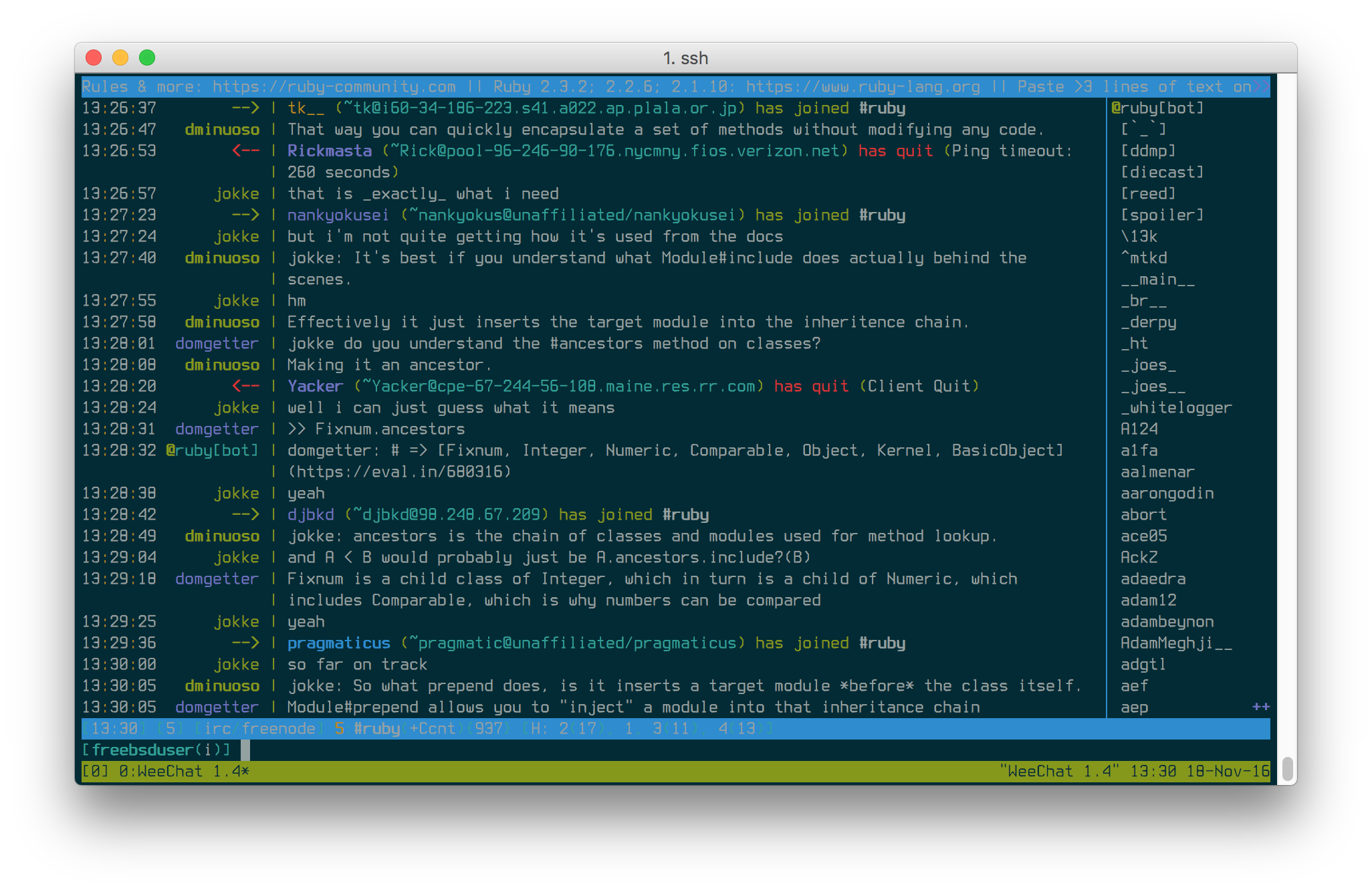
Some keep development services running in a session. Hearty emphasis on development, you probably will want to daemonize and wrap your production web applications, using a tool like supervisor, with its own safe environmental settings.
You can also have multiple users attach their clients to the same sessions, which is great for pair programming. If you were in the same session, you and the other person would see the same thing, share the same input, and the same active window and pane.
The above are just examples; any general workspace you’d normally use in a terminal could work, especially projects or repetitive efforts you multitask on. The tips and tricks section will dive into specific flows you can use today.
Summary
tmux is a versatile addition to your terminal toolbelt. It helps you cover the gaps between multitasking and workspace organization you’d otherwise lose, since there’s no GUI. In addition, it includes a nice ability to detach workspaces to the background and reattach later.
In the next chapter, we will touch on some terminal basics before diving deeper into tmux.