Accessing GitHub using Go
GitHub, like many other sites, uses OAuth 2.0 protocol for authentication. OAuth2 is a protocol that lets external apps request authorization to private details in a user’s GitHub account without getting their password. Applications that need to read or write private information using the API on behalf of another user should use OAuth.
GitHub API
First, read thro’ the GitHub API documentation.
3-legged authorization
On a conceptual level it works in the following way:
- Client has signed up to the GitHub server and got his client credentials (also known as consumer key and secret) ahead of time
- User wants to give the client access to his protected resources on the server
- Client retrieves the temporary credentials (also known as “request token”) from the server
- Client redirects the resource owner to the server
- Resource owner grants the client access to his protected resources on the server
- Server redirects the user back to the client
- Client uses the temporary credentials to retrieve the token credentials (also known as “access token”) from the server
- Client uses the token credentials to access the protected resources on the server
Register your app
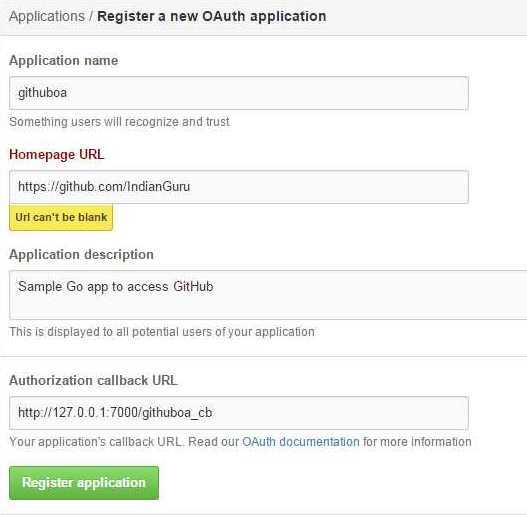
Log into your GitHub a/c and register your app at https://github.com/settings/applications. Click on the “Register new application” button. A registered OAuth application is assigned a unique Client ID and Client Secret. The Client Secret should not be shared. While registering, you can fill out every piece of information however you like, except the Authorization callback URL. This is easily the most important piece to setting up your application. It’s the callback URL that GitHub returns the user to after successful authentication.
I have registered my app githuboa.go at my GitHub a/c.
Register an app